Unit 4
1) What is iOS? Explain features of iOS.
What is iOS?
iOS is a mobile operating system developed by Apple Inc.. It was designed for Apple’s hardware, such as iPhones and iPads. It is the second most popular and widely used mobile operating system globally, after Android. The structure of the iOS operating system is layered, facilitating communication between the Application Layer and the Hardware layer.
Features of iOS
iOS includes a variety of features to enhance user experience and application functionality:
- Multitasking: iOS supports multitasking, allowing applications to run in the background for tasks like audio playback or location updates. It also supports push and local notifications, task completion, and fast app switching.
- Interface: iOS provides a user-friendly interface that utilizes multi-touch gestures such as swipe, tap, and pinch for interacting with applications. It also responds to device movement using internal accelerometers.
- In-App Purchase: This feature allows users to purchase content, subscriptions, services, and new features within applications on various Apple devices.
- Apple Pay: Apple Pay can be integrated into iOS apps for secure payments, authorized via FaceID and TouchID.
- Home Screen: The home screen displays app icons and widgets and includes a dock for frequently used applications. The status bar at the top displays information.
- Notification Center: Introduced in iOS 5, the Notification Center allows users to view a history of their notifications.
- Game Center: Since iOS 4.1, Game Center has provided a social gaming network with features like dashboards, leaderboards, achievements, and multiplayer options.
- Bluetooth: Apple provides the Core Bluetooth framework for connecting with Bluetooth low energy wireless technology.
- Orientations: iOS applications can be used in both portrait and landscape orientations, with size classes in Xcode to help design interfaces for both.
- Camera Integration: The AVFoundation Capture Subsystem provides a high-level architecture for capturing audio, images, and video in iOS.
- Location Services: With user permission, applications and websites can access the device’s location. An icon in the status bar indicates when location services are active.
- Maps: Apple provides a web mapping service that serves as the default map system for iOS, with features like flyover mode. The MapKit framework is used for developing map-based applications.
- Accessibility: iOS offers various accessibility features for individuals with vision and hearing disabilities, such as VoiceOver.
In addition to these, iOS is known for being highly secure compared to other operating systems, having an excellent and fluid UI, being suitable for business and professionals, and generating less heat than Android devices.
2) Explain XCode in iOS.
Xcode in iOS Development
Xcode is an integrated development environment (IDE) developed by Apple, specifically designed for working on Mac operating systems. It contains a suite of software development tools provided by Apple. Xcode facilitates the development of software for various Apple platforms, including macOS, tvOS, iOS, and watchOS.
When you create a new Xcode Project, a window is displayed showing the target information of the project, such as the Bundle Identifier, App version, Build Version, Signing Information, Deployment Information, Linked Binaries and framework information, and application launch icons. Above the target information, there is a pane with project information, including the iOS version for which the application is created and release information.
The Xcode window consists of several key components:
- Standard Editor: Located in the middle of the window, this is the primary area for editing project files, including the initial View Controller class file with lifecycle methods. It also shows hierarchical information about the project file and can be used to open other files.
- Assistant Editor: This editor is mainly used for creating outlets of storyboard components (like Textfields and Labels) in their corresponding View Controller class files. It allows you to view two files simultaneously.
- Project Navigator: Situated on the left side of the window, the project navigator shows the file structure of the project and is used for navigation.
- Inspectors: Shown on the right side of the Xcode window, inspectors provide information and allow modifications. These include:
- File Inspector: Shows information about the opened Swift file, such as Name, Type, Location, and interface builder document details.
- Quick Help Inspector: Provides documentation and help about the syntax.
- Identity Inspector: Used when working with storyboards, it shows information about storyboard components (View Controllers) and their corresponding Swift class files. It’s used to assign class files and identity names to View Controllers and set Runtime constraints to UIViews.
- Attribute Inspector: Used to assign attributes to UIViews in the storyboard, such as content mode, tags, interaction, background color, font color, and font size. These attributes are static but can be changed programmatically.
- Size Inspector: Provides information about the size constraints given to a view when designing with a storyboard and allows altering these constraints.
- Connections Inspector: Shows information about the connections between storyboard UIViews and the Swift class file.
- Media Library: Contains various widgets and objects, such as collection views, that are used to create iOS applications. Items can be inserted into the storyboard using drag and drop.
Xcode is essential for iOS development, providing the necessary tools and environment to build, test, and debug applications for Apple’s mobile devices.
3) Explain iOS architecture.
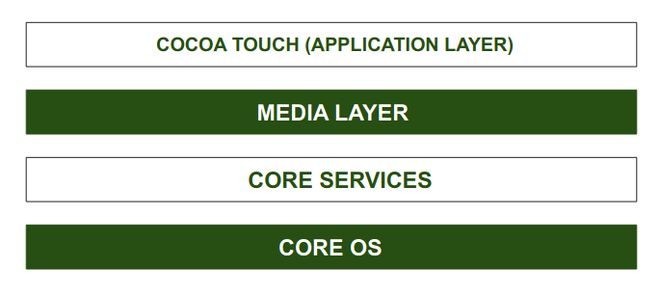
iOS Architecture
The iOS operating system, developed by Apple Inc. for its mobile devices like iPhones and iPads, has a layered architecture. This layered structure facilitates communication between the Application Layer and the Hardware layer, as direct communication does not occur. The architecture is comprised of different layers, where lower levels provide basic services and higher levels provide graphics and interface-related services. Most system interfaces are provided in special packages called frameworks, which contain dynamic shared libraries, header files, images, and helper apps. Each layer has a set of frameworks helpful for developers.
The main layers in the iOS architecture are:
- Core OS Layer: This is the lowest level layer upon which all iOS technologies are built. It includes technologies such as the Core Bluetooth Framework, External Accessories Framework, Accelerate Framework, Security Services Framework, and Local Authorization Framework. It supports 64-bit processing, contributing to faster application performance.
- Core Services Layer: This layer contains important frameworks that contribute to the functionality and maintenance of the iOS operating system. It is the second lowest layer in the architecture. Key frameworks in this layer include:
- Address Book Framework: Provides access to the user’s contact details.
- CloudKit Framework: Provides a way to move data between an app and iCloud.
- Core Data Framework: Used for managing the data model in a Model-View-Controller (MVC) app.
- Core Foundation Framework: Offers data management and service features for iOS applications.
- Core Location Framework: Helps in providing location and heading information to applications.
- Core Motion Framework: Used to access motion-based data on the device.
- Foundation Framework: Covers features found in the Core Foundation framework.
- HealthKit Framework: Handles the user’s health-related information.
- HomeKit Framework: Used for communicating with and controlling connected devices in a user’s home.
- Social Framework: Provides an interface to access users’ social media accounts.
- StoreKit Framework: Supports purchasing content and services from within iOS apps.
- Media Layer: This layer enables the system’s graphics, video, and audio technology. It is the second layer in the architecture. Frameworks in the Media layer include:
- UIKit Graphics: Provides support for designing images and animating view content.
- Core Graphics Framework: Supports 2D vector and image-based rendering and is the native drawing engine for iOS.
- Core Animation: Optimizes the animation experience of apps in iOS.
- Media Player Framework: Provides support for playing playlists and allows access to the user’s iTunes library.
- AVKit: Provides easy-to-use interfaces for video presentation, recording, and playback of audio and video.
- OpenAL: An industry standard technology for providing audio.
- Core Images: Provides advanced support for motionless images.
- GLKit: Manages advanced 2D and 3D rendering through hardware-accelerated interfaces.
- Cocoa Touch: Also known as the application layer, Cocoa Touch acts as an interface for the user to interact with the iOS operating system. It supports touch and motion events and many other features. The Cocoa Touch layer provides frameworks such as:
- EventKit Framework: Shows a standard system interface using view controllers for viewing and changing events.
- GameKit Framework: Provides support for users to share game-related data online using Game Center.
- MapKit Framework: Provides a scrollable map that can be included in an app’s user interface.
- PushKit Framework: Provides registration support.
This layered architecture, with its various frameworks, provides the foundation for developing applications on the iOS platform.
4) Differentiate COCOA and COCOA Touch.
| Feature | Cocoa | Cocoa Touch |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Platform | macOS (Mac OS X) | iOS, iPadOS, watchOS, tvOS |
| Development Focus | Desktop applications | Mobile and wearable applications |
| Key UI Framework | AppKit.framework | UIKit.framework |
| Core Frameworks Included | Foundation, AppKit, CoreData (among others) | Foundation, UIKit, CoreData (among others) |
| User Interaction | Designed for mouse and keyboard input | Optimized for touch-based interactions, smaller screens |
| Relationship | Application framework for Mac OS X | Application framework for iPhone, iPod Touch, etc. Very similar to Cocoa and based on it. |
| Typical Classes | Uses classes like NSButton, NSTextField | Uses classes like UIButton, UITextField |
5) Explain essential COCOA Touch Classes.
- UIView Subclasses: The documents mention
UIViewsubclasses as part of the View layer in the MVC architecture.UIViewis the fundamental building block for visible elements on the screen. Specific examples given or implied in the UI context include:UIButton: Explicitly mentioned in the example differentiating Cocoa and Cocoa Touch code for creating a button. This is an essential class for handling user taps.UILabel: Mentioned as a View object that presents data on the screen in the discussion of the MVC View layer. Essential for displaying static text.UITextField: Mentioned as a View object and also in the context of comparing Cocoa and Cocoa Touch UI classes (NSTextFieldvsUITextField). Essential for text input.
UIViewController: Mentioned multiple times in the documents. View controllers manage the views and the flow of the application’s interface. They are crucial in the MVC pattern, acting as the intermediary between the Model and the View, managing the life cycle of other objects, and containing business logic and navigation.- Foundation Framework Classes: Although also part of Cocoa, Cocoa Touch includes the Foundation framework, which provides fundamental data types, collections, and operating system services. Essential classes here include
NSString,NSArray,NSDictionary, etc., which are fundamental for managing data within any iOS application.
These classes, particularly those from the UIKit framework (UIView, UIViewController, and their subclasses like UIButton, UILabel, UITextField), are essential because they form the basis of the user interface and handle the touch-based interactions that are characteristic of Cocoa Touch applications. The Controller classes (UIViewController subclasses) are essential for managing these views and the application’s logic and flow. Other frameworks within Cocoa Touch provide classes for specific functionalities like graphics (Core Graphics), animation (Core Animation), data management (Core Data), and networking, which are also essential depending on the application’s needs.
6) Explain the concept of MVC Framework.
Based on the provided documents, the Model-View-Controller (MVC) is a commonly used beginner-level software architecture design pattern in iOS application development. It helps in managing the project structure for easier extension and is considered a best practice. MVC is made up of the following three interconnected objects:
-
Model:
- Contains the components that handle the data of the application.
- Responsible for parsing requests and responses with the server’s API.
- Includes elements like persistence logic, model objects (which hold the application’s data), parsers, managers, and networking code.
- Encapsulates the data and the logic used to manipulate it for display.
- Model objects typically have no explicit connection to the user interface that presents the data.
- In dynamic applications using API calls, request and response models are used to parse data.
- Ideally, network communication code resides in a single class for reusability and flexibility.
- Persistence code for local databases also belongs to this layer.
- Abstraction layers and constant files are also considered part of or managed by the Model layer.
-
View:
- Represents the user interface and contains the code to display data from the application’s model to the user.
- Acts as the “face” of the application.
- Objects like
UILabelandUITextFieldare examples of view objects that present data on the screen. - Views are not responsible for storing the data they display, although they might cache repetitive data for performance.
- View objects provided by UIKit are reusable and configurable, ensuring consistency across applications (e.g., a
UIButtonbehaves similarly in different apps). - Views can allow users to edit data and notify the model about these changes.
- The View layer includes
UIViewsubclasses, Core Graphics, Core Animations, and subclasses of Object library widgets.
-
Controller:
- Acts as the intermediary or mediator between the application’s View and Model objects.
- Ensures that the view is displaying the correct model data and that the view interacts correctly with the model classes.
- Manages the life cycle of other objects and coordinates tasks for the application.
- Contains the business logic that defines the application’s functionality.
- Implements delegate and DataSource objects of core view objects like
UITableViewandUICollectionViewfor flexibility. - Defines the navigation between views and determines when to access application data or make network calls.
- It is often considered the least reusable part of the application as it involves domain-specific code.
- The controller can be seen as the “brain” or “engine” of the application.
In the MVC pattern, the Controller updates the View when the Model changes and updates the Model when the View interacts with the user (e.g., through user input). The Model notifies the Controller when its data changes. This separation of concerns helps in organizing code, making it more maintainable and testable.
7) Explain advantages and disadvantages of iOS.
Advantages of iOS:
- More Secure: iOS is highlighted as being more secure than other operating systems.
- Excellent UI and Fluid Responsive: It offers a superior user interface and is described as fluid and responsive.
- Suits Best for Business and Professionals: iOS is presented as being well-suited for business and professional use.
- Generate Less Heat: Compared to Android, iOS devices are noted to generate less heat.
Disadvantages of iOS:
- More Costly: iOS devices are generally more expensive.
- Less User Friendly: Compared to the Android operating system, iOS is considered less user-friendly by the document.
- Not Flexible: It is less flexible as it exclusively supports iOS devices.
- Battery Performance is Poor: The battery performance of iOS devices is described as poor.
8) Explain Project Navigator, File Inspector, Quick help inspector in terms of X-CODE.
Based on the provided documents, here are explanations of the Project Navigator, File Inspector, and Quick Help Inspector within Xcode:
Project Navigator
- The Project Navigator is located on the left side of the Xcode window.
- Its primary function is to show the file structure of the project.
- It is used to navigate through the project files and folders. When you initially create an Xcode project, the Project Navigator displays the default set of files included in the project.
File Inspector
- The File Inspector is one of the inspectors shown on the right side of the Xcode window.
- It displays full information about the corresponding file that is currently opened in the standard editor (e.g., a Swift file).
- Information provided by the File Inspector includes the Name, Type, Location of the file, and details related to the interface builder document if applicable.
Quick Help Inspector
- The Quick Help Inspector is also located among the inspectors on the right side of the Xcode window.
- Its purpose is to provide help and documentation to the user.
- You can use it to search the documentation about the syntax of code elements you select in the editor. This is helpful for understanding how to use classes, methods, properties, and other programming constructs.